Their impact is thought to account for many times more than that of scope 1 and scope 2 emissions. Often hard to measure and report, they have become a hot topic with regulations and legislation on the horizon in both the E.U. and the U.S. According to research firm Verdantix, climate disclosures are a top priority for corporate ESG and Sustainability spending. How can companies get to grips with scope 3 emissions reporting?
What are scope 3 emissions?
Scope 3 emissions are all the carbon consumed, used, and emitted in the entire lifecycle of a company and its products and services outside of the direct company footprint. It is all the emissions from its suppliers and distributors as well as the impact products and services themselves have on the environment in their natural lifespan.
Examples of scope 3 emissions include:
- Extraction, production and transportation of good and services in the supply chain
- Fuel, electricity, and bi-product lifecycle in the company’s value chain
- Transport and distribution of products and services for production and supply
- Disposal and treatment of waste
- Employee commuting and business travel in supplier companies
- Emissions from the use of products or services
- Downstream factors such emissions from leased assets, franchises or investments involving third parties
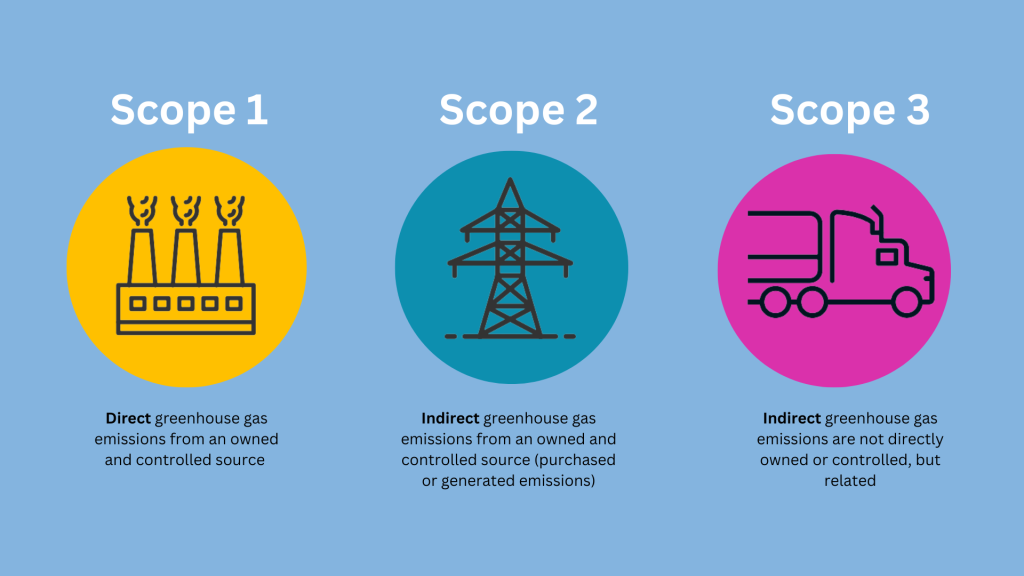
Why is scope 3 important?
As the impact of climate change is becoming more evident across the globe, governments are investing heavily to transform the way their country interacts with its environment. Regulation and legislation are catching up with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive in the EU and the proposed SEC climate disclosure rule in the U.S., mandating the accurate and auditable filing of ESG disclosures.
Investors now expect enterprises to be doing the same and are placing increased emphasis on analyzing ESG disclosures as critical decision factors. The performance of an enterprise determined through its disclosures is now linked heavily to an assessment of the material ESG risks a company will face in the future and how well prepared they are to respond. Enterprises that score well are seen as better prospects for long-term investments.
The challenge with scope 3
Global enterprises have the hard task of measuring, reporting, and working out plans to reduce their carbon emissions. It’s a hard enough task to gather, collect, cleanse, and transform scope 1 and 2 emissions data that you own.
But the real challenge is measuring and reporting on the carbon impact from external suppliers, partners, and customers. This scope 3 emissions data do not reside in your IT domain or within your control. Do you have access to all the data? Can you trust the data when manually reported without auditable source records?
Many companies have resorted to making estimations or forecasts for scope 3 based on available methodologies rather than based on actual data. This gives no actual insight into whether scope 3 performance is good, bad, or worrisome. In fact, it gives no insight to the actual impact the company is having on the planet in its total sphere of operation.
There’s a new way
Companies need to orchestrate, automate, and federate scope 3 data to ensure reporting compliance and drive their emissions program. YuzeData supports customers with out-of-the-box functionality:
- ESG connectors pre-mapped for scope 3
- Edge orchestration - integrate data from any source
- A library of pre-built scope 3 use case templates compliant to multiple standards
- Build your own automations from scratch or clone our templates
- Publish and share templates across your business
- Add domain knowledge and context to the data
- Federate the data between reporting company and your value chain
- Automate the push of scope 3 data into the ESG reporting tool of your choice
Scope 3 emissions reporting is hard. Federated collaboration and sharing across your value chain make it a lot easier. Don’t let your data make you work hard; make your data work hard for you!